BUS SIMULATION
SCENARIOS
HOW IT WORKS
The Spine Metaphor: The central bus acts as the backbone, connecting all components.
Red Dots (Address Bus): Components asking "Where is the data?" or "Where should I put this?"
Yellow Dots (Data Bus): The actual information (numbers, letters, graphics) moving between components.
COMMODORE 64 HARDWARE
The C64C motherboard with key chips labeled. The C64's architecture is elegantly simple yet powerful.
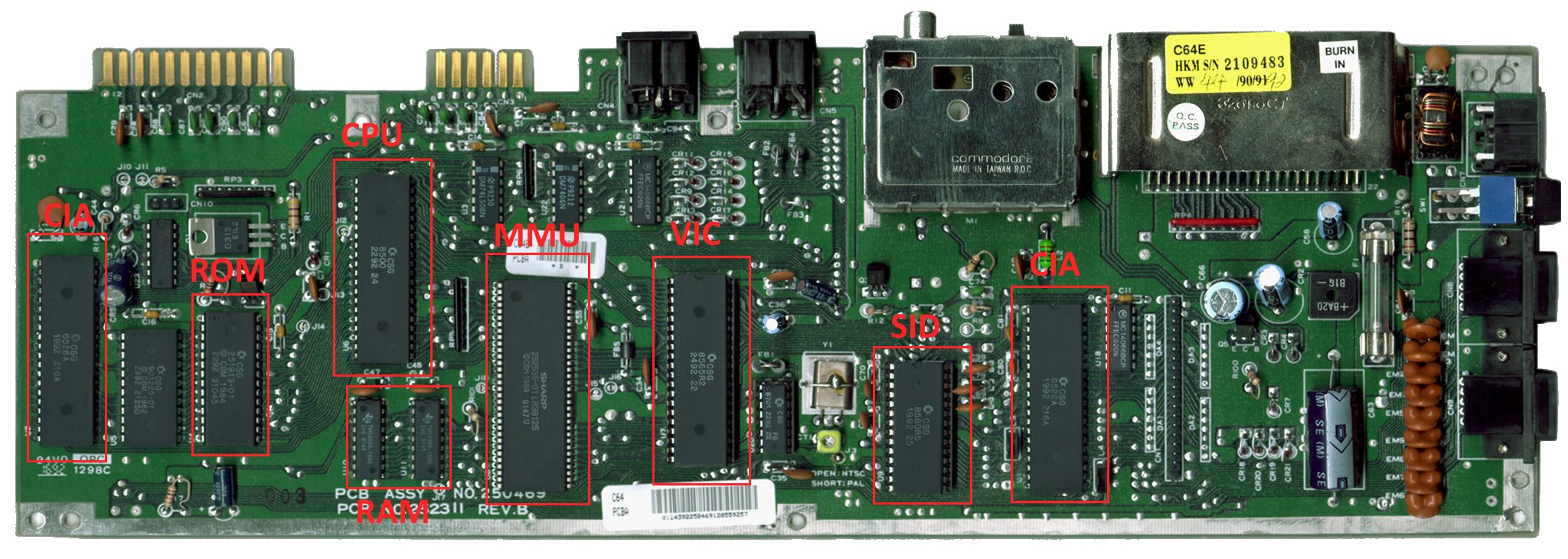
CHIP REFERENCE
CPU
The brain of the C64. An enhanced 6502 with built-in I/O port for bank switching.
- Part: 6510 / 8500
- Clock: ~1 MHz
- Address Bus: 16-bit (64KB)
- Data Bus: 8-bit
VIC-II
Handles all graphics: sprites, characters, bitmaps. Can steal bus cycles from CPU.
- Part: 6569 (PAL) / 6567 (NTSC)
- Resolution: 320×200 / 160×200
- Colors: 16
- Sprites: 8 hardware
SID
The legendary sound chip that made C64 music famous worldwide.
- Part: 6581 (12V) / 8580 (9V)
- Voices: 3 independent
- Waveforms: 4 types
- Filters: Programmable
CIA 1
Complex Interface Adapter handling keyboard scanning and joystick ports.
- Part: 6526 / 8521
- Function: Keyboard/Joystick
- Timers: 2 × 16-bit
- I/O Ports: 2 × 8-bit
CIA 2
Second CIA chip controlling serial bus, user port, and VIC bank selection.
- Part: 6526 / 8521
- Function: Serial/User port
- VIC Bank: Selects 16KB bank
- Timers: 2 × 16-bit
MMU
Memory Management Unit / PLA. The traffic controller deciding which chip responds to each address.
- Part: 906114 / 252535
- Function: Address decode
- Controls: Bank switching
- Note: Runs hot, common failure
ROM
Contains KERNAL OS, BASIC interpreter, and character sets. Combined in one chip on C64C.
- Part: 251913-01 (C64C)
- KERNAL: 8 KB ($E000-$FFFF)
- BASIC: 8 KB ($A000-$BFFF)
- CHAROM: 4 KB ($D000-$DFFF)
RAM
Two 4464 chips providing 64KB of dynamic RAM, shared between CPU and VIC-II.
- Part: 4464 × 2 (C64C)
- Size: 64 KB total
- Type: Dynamic RAM
- Shared: CPU & VIC-II